BioGPT: Generative Pre-trained Transformer for Biomedical Text Mining
Following the recent breakthrough in Natural Language Processing models, everyone is now talking about Transformers and ChatGPT. I wondered whether some models had been trained for use in biology or bioinformatics. I discovered a research project called BioGPT developped by Microsoft. This article to both describe BioGPT and summarise the recent history of Transformers and NLP.
Bibliography is Hard Work (and is getting worse)
The PubMed database contains more than 36 million publications. Every year this number increases following an exponential growth.
They are no universal glossary e.g. a drug can have multiple synonyms depending on the field, the time frame, the country, etc. So, the research by keyword may be incomplete and not cover all the related articles. In addition, articles are sorted by field or key words making any cross-disciplinary research tedious.
Natural Language Processing
NLP are methods to give the computer the ability to understand and speak human language. BioGPT is a model trained on the content of all available articles in PubMed.
BioGPT can do:
- Answer question using PubMed materials
- Find drugs relations using PubMed materials
History of NLP
- In the early 20th century, Ferdinand de Saussure establishes human language as a logical structure.
- In 1952, Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley discover neural networks (Nobel Medicine 1963).
These events inspire the idea of a machine able to speak and understand human language.
Alan Turing stated that if a machine could chat with you and you can’t tell it apart from a human, then the machine could be considered capable of thinking.
Boolean request
Boolean logic involves TRUE or FALSE answer. The found documents are the ones matching an exact term. To go further, you can combine statements OR, AND, NEAR.
Example: in a search engine, you type "puppy" and "kitten" to find any documents that contains both "puppy" and "kitten".
Terms frequency
Term frequency: How often appears a word in a document.
Inverse Document frequency: importance of a word in multiple documents.
Term frequency identifies important word that are both frequent in a document and rare across the dataset. It ignores common words like “the” or “is” as well.
Example: Tag cloud.
Co-occurence matrix
Co-occurence matrix is the table of the number of times two words appear together. The aim is to find words significantly associated. It is possible to reduce a set of words into a set of vector of associated words in order to process vector of words instead of words.
Example:
Apples are green and red.
Red apples are sweet.
Green oranges are sour.
| - | apples | green | red | sweet | oranges | sour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
apples | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
green | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
red | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
sweet | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
oranges | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
sour | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
In this text, red and apples are associated while sour and apples are not.
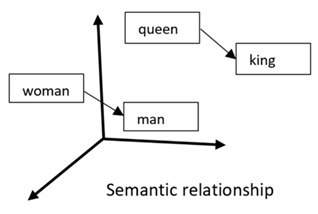
Word2vec: Word to Vector
A word is considered as a vector. The computer follows an unsupervised learning (~no involved human) from the document. Each surrounding words is a context or bag of words teaching the word to predict given the context. The sum of all predictions produce a vector space or semantic relationship.
Example:
The computer understand from a document that the word queen and king are linked and woman and man relationship are aligned with king and woman relationship. By summing the vectors, the computer can deduce association between queen and woman and king and man.
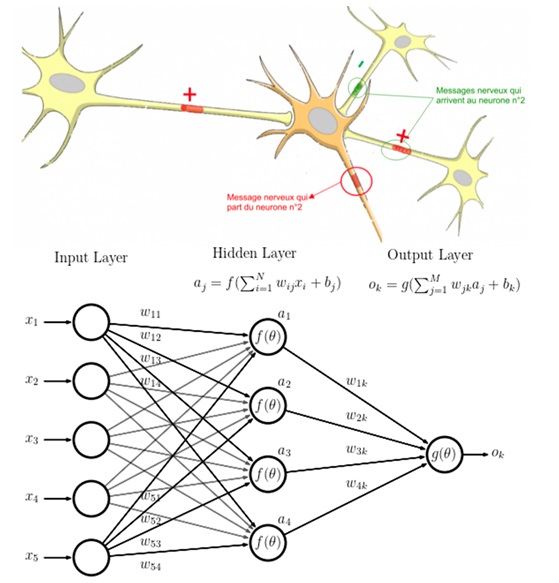
Neural Network
Inspired by human brain, they are interconnected neurons organised into layers (input, hidden and output). Each connection between neuron has a weight. The network is trained on documents to adjust weights. Weights are self-corrected to minimise the difference between the prediction and the expected result.
Example: Word2vec is based on neural network of three layers.
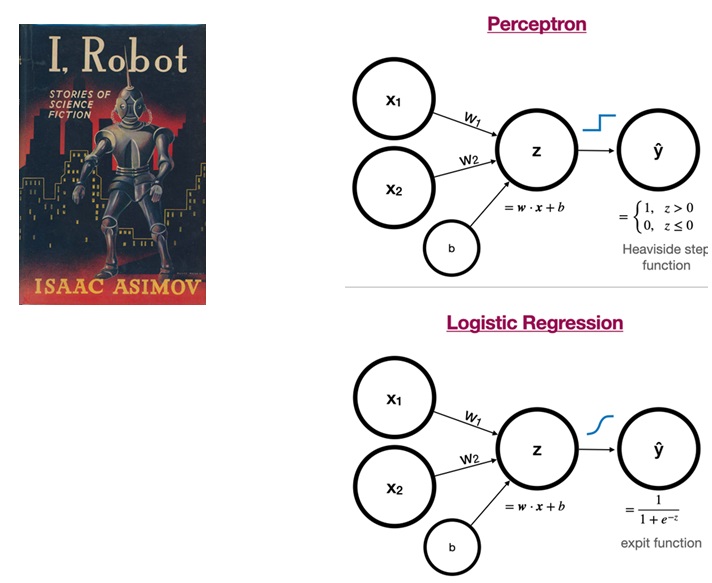
Perceptron
Designed in 1969 with the idea of creating a robot in the image of human. The perceptron is a neural network of 2 layers: input and output.
💡 Note: Without the hidden layer, a neural network is a logistic regression model (Berkson et al. 1944) with a Boolean output.
Transformer
The transformer is a neural network with four layers. It adds a a new intermediate layer called attention (Vaswani et al. 2017). The decoder layer transforms the input document into a bag of words. The encoder layer produces a predicted vector of words using word2vec. Attention assigns weights to link the encoder and decoder layers. The transformer is the state-of-the-art method in natural language processing. BERT and GPT are based on transformer.
Example: deepL for document translation.
Bidirectionnel Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
Transformer architecture developed by Google in 2018. In France, Martin et al. developed camembert in 2019. The context is processed twice from right to left and from left to right. Pre-trained: the neural network is already weighted based on a training using a HUGE dataset so it can be fine-tuned for specific use.
Example: Google Search when you type a full sentence.
Can google find my missing sock?
People also ask
How do I find my lost sock?
When socks disappear where do they go?
Why can't I find my socks?
Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT)
Transformer architecture developed by openAI in 2020. Contrary to BERT, the document is processed with an unidirectional attention. In addition, the pre-training is different between GPT and BERT. While BERT is trained to predict the missing word giving a context, GPT is trained to generate complete comprehensive sentence giving a context.
Example: chatGPT
BioGPT
- BioGPT is a GPT model fine-tuned based on PubMed publications.
- Microsoft provided the source code to build a bioGPT software: github source code BioGPT
- The 🤗 Hugging Face is an online library of all natural language processing neural network models including transformers including BioGPT.
Conclusion
Transformer models are not trained on human words but on token. Token are the unit of chunks of information extracted from the original document. They are not human readable. Purely black box machine abstraction. Computer language comprehension relies on maths, not on real text comprehension. On the other side, we could say human language comprehension relies on neurotransmitter concentration. The point is the computer and the human are able to understand each other.
BioGPT is based on biomedical dataset so this is not relevant for other fields yet. For instance if I ask information about the sugar beet to BioGPT, he will give only information related to human nutrition. BioGPT is specialized into biomedical data and nothing else. Can we imagine a similar AI based on crop science literature in the future? The hardest part will be to collect and format relevant crop science text material.
References
BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining
Renquian Luo, Liai Sun, Yingce Xia, Tao Qin, Sheng Zhang, Hoifung Poon, Tie-Yan Liu
Briefings in Bioinformatics, November 2022. DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbac409
Hugging Face
Jain, S.M.
Introduction to Transformers for NLP. Apress, Berkeley, CA, october 2022. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4842-8844-3_4
CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model
Louis Martin, Benjamin Muller, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah, Benoît Sagot
Submitted in november 2019. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1911.03894
Attention is All you Need
Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N Gomez, Łukasz Kaiser, Illia Polosukhin
Neural information processing systems, december 2017. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762
Word2Vec
Kenneth Ward Church
Natural Language Engineering, january 2017. DOI: 10.1017/S1351324916000334
The Perceptron: A Model for Brain Functioning
H.D. Block
Reviews of Modern Physics, january 1962. DOI: 10.1103/RevModPhys.34.123
Propagation of electrical signals along giant nerve fibres
Alan Lloyd Hodgkin and Andrew Fielding Huxley
Processdings of The Royal Society B, october 1952. DOI: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0054
Relevant Tags
About the Author
Latest Articles
-
Research Tax Credit
The Research Activities Tax Credit is a tax credit that incentivizes private companies to increase their Research and Development (R&D). Within my company, I have been tasked with writing the Research Tax Credit (CIR) justification report for France. Here, the method for writing such a report.OCT 2025 · PIERRE-EDOUARD GUERIN -
Turing Complete: From Logical Gates to CPU Architecture
In 2021, LevelHead published Turing Complete, a game about computer science. My friend Christophe Georgescu recommended me to play it. Unfortunately, I took his advice and now I can not stop to play this game! The game challenges you to design an entire computer from scratch. You start with basic logic gates, then move on to components, memory, CPU architecture, and finally assembly programming. By the way, the game is neat and present all these concepts in a playful and intuitive way.SEP 2025 · PIERRE-EDOUARD GUERIN -
How to Manage a Project?
In any company, every task is part of a project. I am responsible for managing multiple projects each year. I have to present deliverables to stakeholders, meet deadlines, allocate mandays and coordinate everyone’s actions. This is a meticulous work that requires a strong methodology.JUN 2025 · PIERRE-EDOUARD GUERIN